Audio Source Component
Each audio source is a node on a graph inside an Audio Engine. You can connect them however you like and apply different effects
Usage
Initialize
Add component AudioSourceComponent to your entity
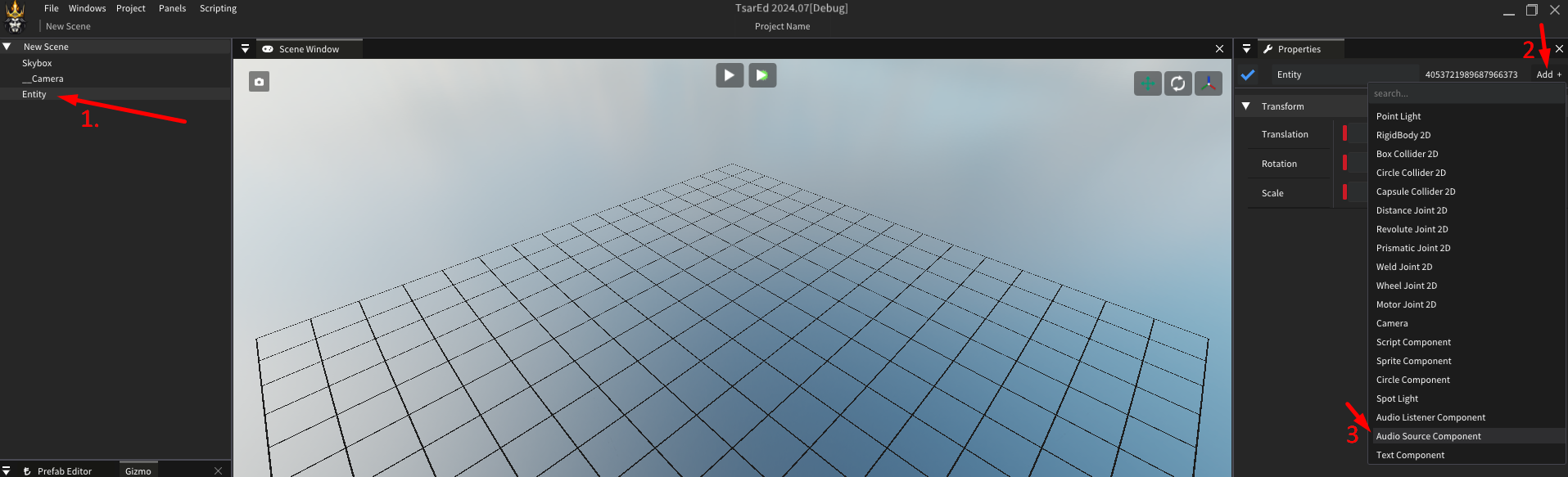 Click 'Find' button and navigate to desired audio clip
Click 'Find' button and navigate to desired audio clip
Audio Clip
To have actual sound it needs an Audio Clip. You can assign one by Drag-n-Drop from Content Browser.
An audio clip is audio file stored on disk/drive. This is your typical sound effect or music.
Tsar currently supports WAV and MP3 file formats.
Audio clip is the source of sound which is "fed" to Audio Source, which then does some processing with it.
You can imagine Audio Clip to be a book and Audio Source to be a reader.
To improve performance Audio Clip has loading flags specified in Audio Source Component.
IsLoadedAsync
- TRUE : Load audio in background without blocking, loading returns immediatly and you can call Play() right away, but sound will be heard after something is loaded.
- FALSE : Load audio before doing anything else, loading blocks until whole clip is loaded.
IsAudioStreamed
- TRUE : Load small chunk of audio(2 seconds by default), when new data is required, load again. This is useful for music(long audio) or if you don't know the length of what you process(like audio over internet).
- FALSE : Load whole clip into memory, this is preferred for smaller files, like SFX.
Audio Clip is loaded only once unless you change the clip during Runtime or Audio Source has IsAudioStreamed=true.
MaxSounds
How much simultanous sounds can be played from same source. To reduce memory usage, this is a mechanism for managing SFX on low level, by limiting independant buffers, otherwise you have to wait the sound to reach end or rewind it back to start.
Volume
void SetVolume(float volume, bool IsVolumeInDecibels = true)
AudioSource src = GetComponent<AudioSource>();
src.SetVolume(10.0f); //Set volume of sound to 10 decibels
src.SetVolume(100.0f, false); //Set linear volume of sound to 20 decibels.
//See linear to db conversion
void IncreaseVolume(float volumePercentIncrease, bool IsVolumeInDecibels = true)
AudioSource src = GetComponent<AudioSource>();
src.IncreaseVolume(10.0f); //Increase current volume by 10% in decibels 10db->11db
src.IncreaseVolume(10.0f, false); //Increase current volume by 10 decibels.
//Doesn't scale linearly, see linear to db conversion
void DecreaseVolume(float volumePercentDecrease, bool IsVolumeInDecibels = true)
AudioSource src = GetComponent<AudioSource>();
src.DecreaseVolume(30.0f); //Reduce current volume by 30% 10db->7db
src.DecreaseVolume(100.0f, false); //Reduce current volume by 20db