Scripting
Tsar uses C++ as scripting language to benefit from its unmatched speed and versatility as its the best OOP language.
Writing scripts is essential for creating immersive and complex games. All of your game logic will be modeled by your scripts.
For this reason our scripting interface is focused on simplicity.
Here's an example NPC logic script: 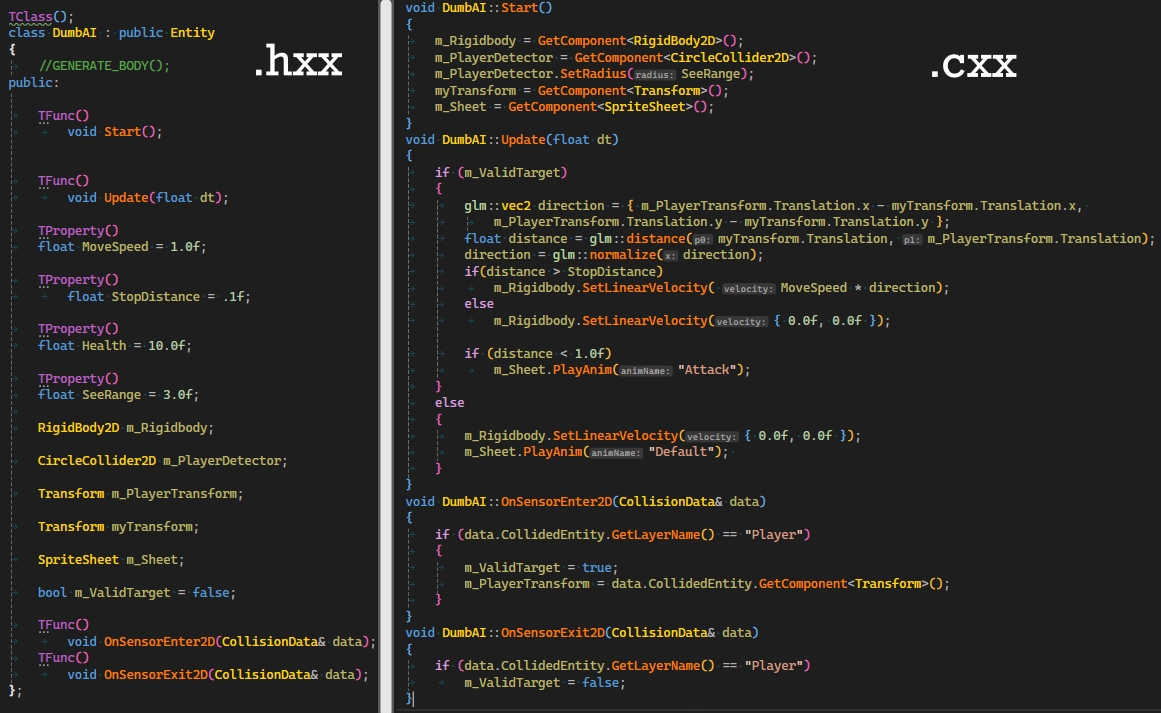
How to create a script
!!! Make sure you have a scripting project, if not generate it by executing this script:TsarEd\assets\scripts\GenProject.py
You should now have a default Sandbox solution
Using Editor
Soon to be supported!
Using Visual Studio
1. Navigate your source folder and create .hxx and .cxx files with desired name2. In the header file(.hxx) add your class following this pattern:
MyExampleClass.hxx
#include "ScriptEngine.hxx"
namespace TsarScript
{
TClass() // <-- this macro is used to register your class in Tsar
class MyExampleClass : public Entity//if you want your class to interract with Tsar
{
TFunc()// <-- this macro is used to allow access of your func to Tsar
void SomePrintFunc();
};
TClass()
class MyPlayer : public Entity
{
GENERATE_BODY()
private:
TFunc()
void Start();
TFunc()
void Update(float dt);
private:
Transform m_MyTransform; //every Entity has Transform
};
}
Change MyExampleClass with your script/class name, you can have as many classes you want in single header.
TClass() is used for Reflection so Tsar and your classes can work together.
3. In source file(.cxx) include your header and define your functions:
MyExampleClass.cxx
#include "MyExampleClass.hxx"
#include "scripting/Input.hxx" //for MyPlayer input
#include "scripting/Debug.hxx" //for MyClassExample
namespace TsarScript
{
void MyClassExample::SomePrintFunc()
{
Debug::LogInfo("something happened");
}
void MyPlayer::Start()
{
//Good practise is to get you components once at Start, if possible
m_MyTransform = GetComponent<Transform>();
}
void MyPlayer::Update(float dt)
{
if (Input::GetKeyPressed(KeyCode::T))
{
Debug::LogInfo(m_Entity.GetName());// Log Entity name
}
}
}
Adding Functions/Methods
There are two types of functions/methods: Reflective and Normal.Normal functions are your typical C++ methods, which Tsar knows nothing about.
void MyFunction(); // No engine context here
If you need your function to be seen by Tsar you should use Reflective functions/methods, which are declared with TFunc() before them like this:
TFunc()
void MyFunction(); // Can use engine functionality
If your function should access anything from Tsar, like components, scripts, assets you must define your function with TFunc().
If the function is purely C++ logic, you don’t need TFunc().
Adding Properties
Similar to functions, Properties can use reflection, but mainly for modification in Editor.For example, take this AudioSource component
TClass();
class DumbAI : public Entity
{
public:
AudioSource m_BigSwing; //Not seen in Editor
};
Written like that AudioSource cannot be assigned/referenced/modified from Editor, you can only get this component from code with GetComponent(), if its assigned on the same Entity the script is assigned to.
If you want to expose the Property to Editor use TProperty() before declaration. This way you don't need to call GetComponent() in code.
TClass();
class DumbAI : public Entity
{
public:
TProperty();
AudioSource m_BigSwing; //Modifiable in Editor
};
Physics Event Callbacks
There are two types of events: Enter and Exit.For 2D physics there are three conditions triggering each event: Collision, Hit and Sensor
- Collision Event is when two shapes on differnet rigidbodies start/stop touching each other. These shapes must not be sensors.
- Hit Event is when two shapes on different bodies collide with velocity/speed above specified threshold. Hit Event requires collision events to be enabled/working.
- Sensor Event is when two shapes on different bodies, one of which is sensor (hollow. not solid) overlap. Sensor shapes don't provide collision so they overlap with other shapes.
Implementing callbacks is easy, first you have to declare it in .hxx file
TFunc()
void OnSensorEnter2D(CollisionData& data);
TFunc()
void OnSensorExit2D(CollisionData& data);
Then you can write your implementation logic in .cxx file. Below is partial example of jump logic which when Player sensor overlaps(Enter Event) with Ground(which is not sensor), the Player becomes 'grounded' and when Player is no longer overlapping(Exit Event) with Ground, Player is 'ungrounded'.
void Player::OnSensorEnter2D(CollisionData& data)
{
if(data.CollidedEntity.GetLayerName() == "Ground")
m_Grounded = true;
}
void Player::OnSensorExit2D(CollisionData& data)
{
if(data.CollidedEntity.GetLayerName() == "Ground")
m_Grounded = false;
}