Wheel Joint2D Component
The WheelJoint2D class is a component in Tsar engine used to define a joint connection between two Rigidbody2D.
The joint has to reference another Entity which has Rigidbody2D Component.
The wheel joint combines PrismaticJoint2D, RevoluteJoint2D with spring/damper and motor.
WheelJoint2D has limited axis on which the 'Wheel' can move along with spring damping, the 'Wheel' can rotate, essentially a full suspension joint.
Can use motor and translation limits.
Joint Scheme
Demonstration
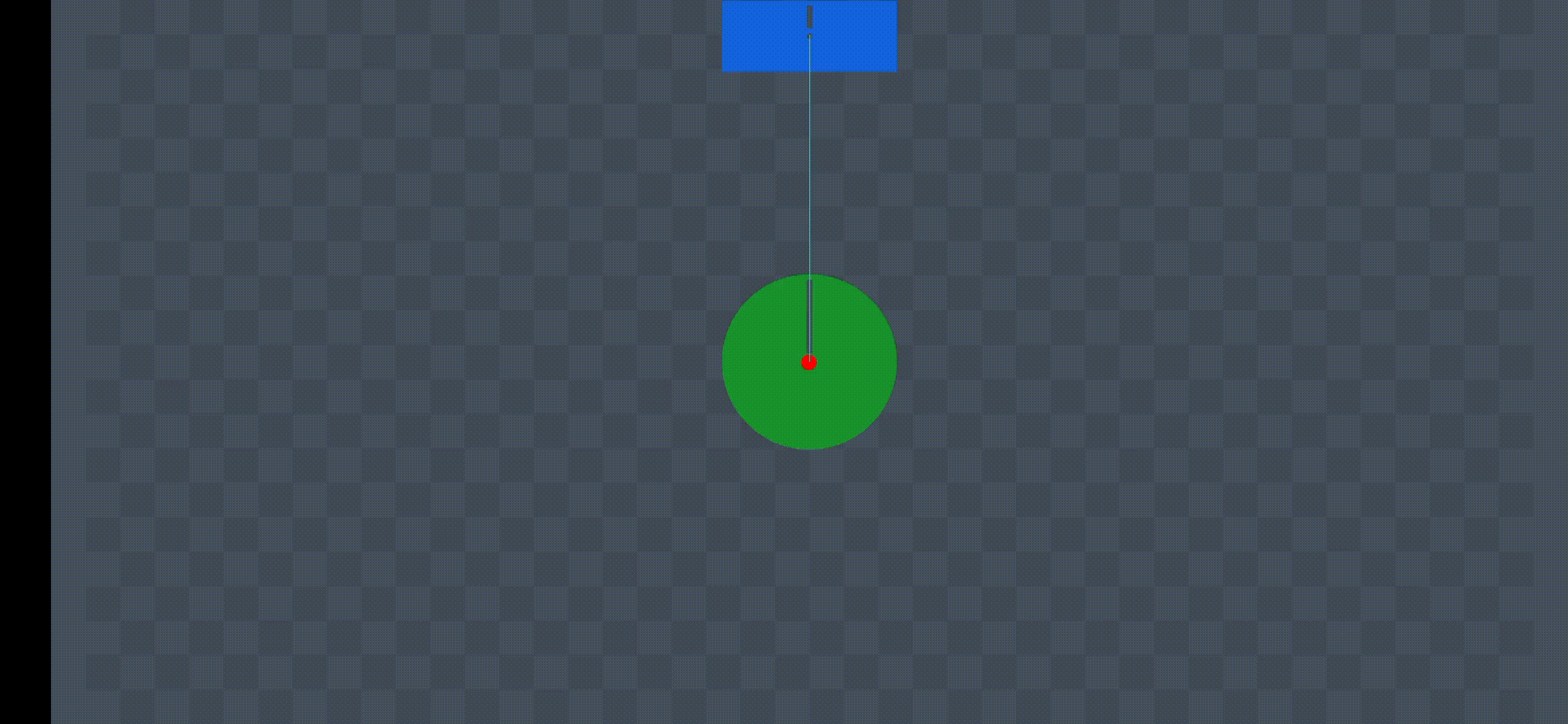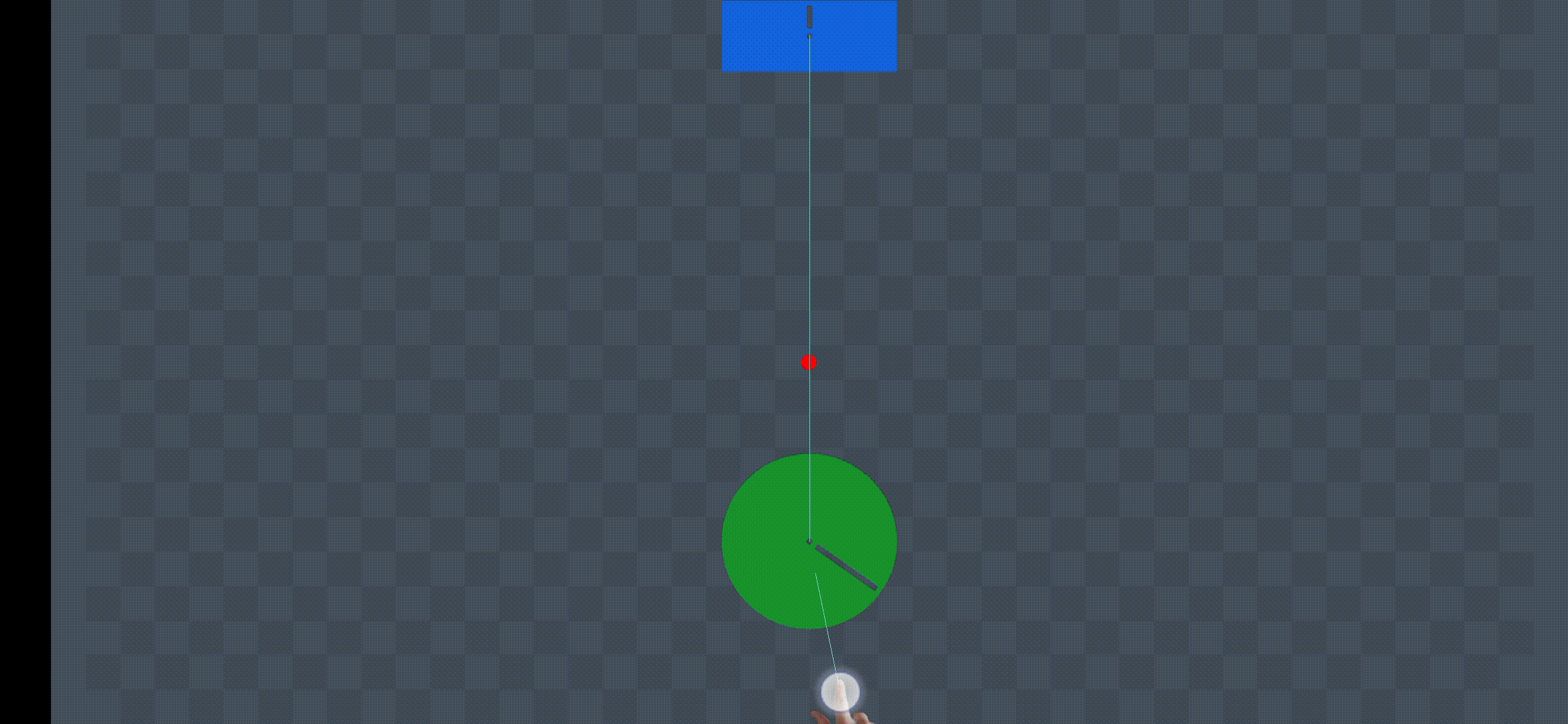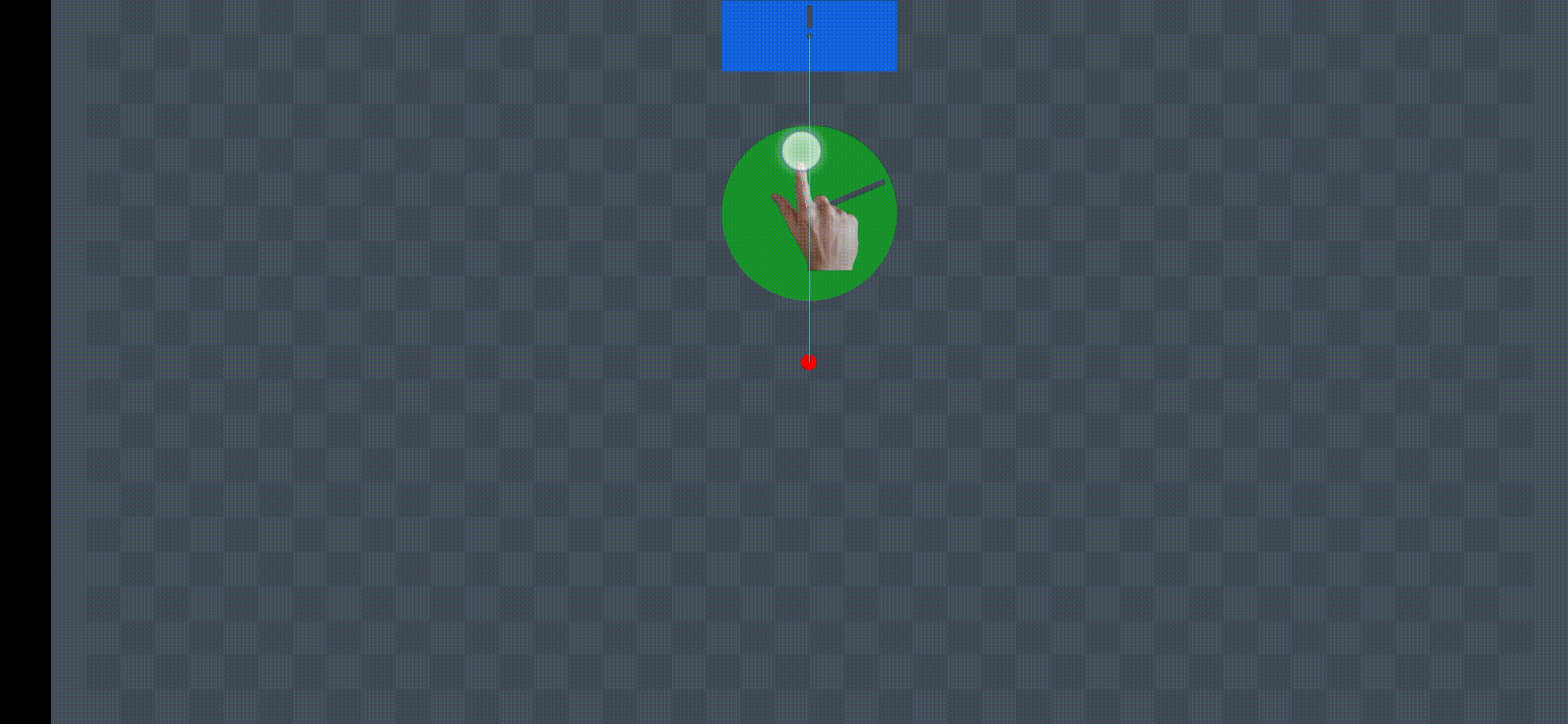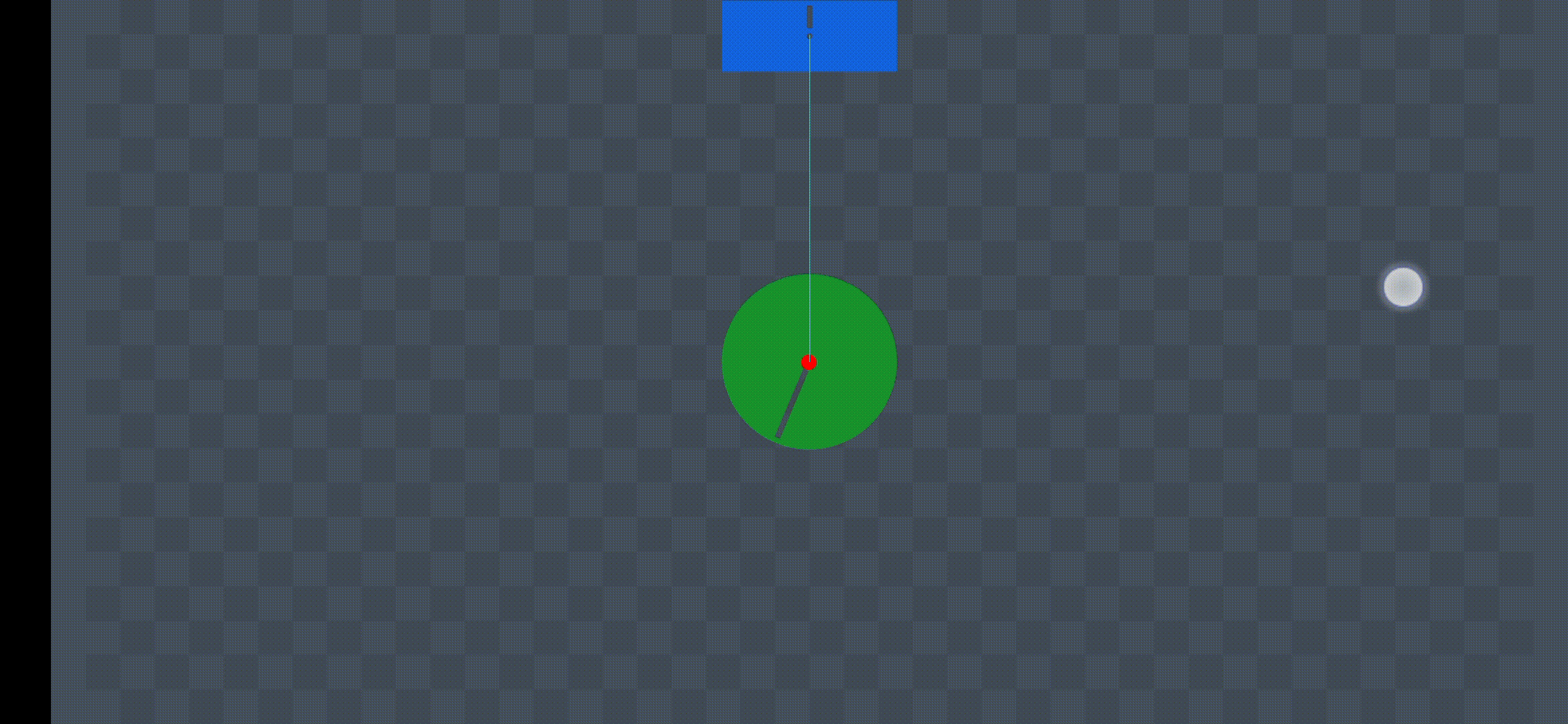
Animation Source: https://miro.medium.com/v2/resize:fit:720/format:webp/1*L7W3ya854UGntCk0Yk5Plw.gif
Class Declaration
class WheelJoint2D : public Component
This class inherits from the Component class and adds functionality related to defining a revolute joint connection to another Rigidbody2D for simulating 2D physics.
Public Methods
Attach
bool AttachToBody(RigidBody2D& referenceBody)
Attach the joint to Entity which has the referenced Rigidbody2D. One joint component can only have one attached Rigidbody2D.
Attaching when existing joint is present will destroy the old one.
Requires valid Rigidbody2D on both entities.
- referenceBody - the Rigidbody2D component to which the joint will be attached.
Returns:
- true if joint was created successfuly.
- false if joint creation failed.
bool AttachToEntity(u64 entityID)
Attach joint directly using Entity. Requires valid Rigidbody2D on Entity.
- entityID - id of entity to which to attach joint connection.
Returns:
- true if joint was created successfuly.
- false if joint creation failed.
bool DetachFromBody()
Destroys the joint connection.
Returns:
- true if joint has been destroyed.
- false if no joint was destroyed.
Properties
The WheelJoint2D class exposes properties (that can also be accessed via getter and setter functions).
These properties allow users to manipulate the joint properties in a more intuitive manner:
glm::vec2 MountPoint
Position offset of the mounting point of suspension on same Entity which has the WheelJoint2D.
- Get:
glm::vec2 GetMountPoint() - Set:
SetMountPoint(const glm::vec2& posLocalOffset)
float WheelOffset
Position offset from referenced body, defining axle of the wheel. {0; 0} for center of referenced Rigidbody2D.
- Get:
float GetWheelOffset() - Set:
void SetWheelOffset(const glm::vec2& pLocalOffset)- pLocalOffset - local space offset of wheel center point.
bool CollideWithOther
Should the colliders attached to both bodies collide with each other?
- Get:
bool GetCollideWithOther() - Set:
void SetCollideWithOther(bool collide)- collide - true makes bodies collide with each other, false disables collision between them.
bool IsMotorEnabled
Enable/Disable motor. If you enable the motor, Box2D will apply torque to reach and maintain a given angular speed (MotorSpeed), up to a specified maximum torque (MaxMotorTorque).
- Get:
bool IsMotorEnabled() - Set:
void EnableMotor(bool enable)- enable - true enables motor, false disables motor.
bool IsSpringEnabled
Enable/Disable spring. Spring acts on constrained LimitedAxis, as suspension spring on a vehicle.
When disabled, frequency=0 and dampingRatio=1.
- Get:
bool IsSpringEnabled() - Set:
void EnableSpring(bool enable)- enable - true enables spring, false disables spring.
bool IsLimitEnabled
Enable/Disable limit. Limits suspension travel.
- Get:
bool IsLimitEnabled() - Set:
void EnableLimit(bool enable)- enable - true enables suspension limit, false disables limit.
float SpringFrequency
If IsSpingEnabled = true, this acts as spring trying to maintain distance between MountPoint and WheelOffset in elastic manner.
Frequency (or spring linear stiffness) is in Hertz(HZ), cycles per second.
For better stability should usually be less than a quarter of the simulation rate. For example, if the simulation runs at 60Hz then the joint stiffness should be 15Hz or less.
- Get:
float GetSpringFrequencyHZ() - Set:
void SetSpringFrequencyHZ(float freq)- freq - should be non-negative value.
float SpringDampingRatio
Linear damping ratio of spring, non-dimensional, how much the suspension resists oscillation.
0 means no damping (energy loss) and 1 means full absorbtion (immediate energy loss).
- Get:
float GetSpringDampingRatio() - Set:
void SetSpringDampingRatio(float ratio)- ratio - value in range [0; 1].
float UpperTranslationLimit
When IsLimitEnabled=true, this specifies maximum translation distance possible between two bodies (suspension max travel), in meters. Cannot extend beyond set length.
The joint translation is zero when the local anchor points coincide in world space.
- Get:
float GetUpperTranslationLimit() - Set:
void SetUpperTranslationLimit(float maxDist)- maxDist - must be greater than LowerTranslationLimit, in meters.
float LowerTranslationLimit
When IsLimitEnabled=true, this specifies minimum translation distance possible between two bodies (suspension min travel), in meters. Cannot compress below set length.
The joint translation is zero when the local anchor points coincide in world space.
- Get:
float LowerTranslationLimit() - Set:
void SetLowerTranslationLimit(float minDist)- maxDist - must be less than UpperTranslationLimit, in meters.
float MotorSpeed
When IsMotor=true, this specifies the speed at which the joint rotates the dynamic body ('Wheel') along Z-axis in radians per second.
This speed won't be reached if MaxTorque is not strong enough.
Positive value rotates counter-clockwise, negative value rotates clockwise.
- Get:
float GetMotorSpeed() - Set:
void SetMotorSpeed(float motorSpeed)- motorSpeed - radians per second.
float MaxMotorTorque
When IsMotor=true, this specifies the maximum torque (angular force) the motor will apply to 'Wheel', in Newton-meters.
Note the mass of bodies for better tuning and colliders material settings.
- Get:
float GetMaxMotorTorque() - Set:
void SetMaxMotorTorque(float torque)- torque - non-negative value in Newton-meters.